Fungal skin infections are among the most widespread dermatological issues worldwide, affecting millions of people annually. They are caused by various fungi that thrive in warm, moist environments and can impact skin, nails, and hair.
Superficial fungal infections affect the global population, making them one of the most prevalent conditions in dermatology. These infections are generally not life-threatening but can cause significant discomfort and require proper treatment.
In this blog, we will explore what fungal skin infections are and go over the types, causes, and treatments you must know so you can identify them early and seek proper care.
What are Fungal Skin Infections
Such infections occur when fungi invade and multiply on the skin’s surface. These infections often thrive in damp areas of the body, such as the feet, groin, or armpits. Common symptoms include itching, redness, peeling, or the formation of circular rashes.
They can range from mild to more severe, depending on the type of fungus and the individual’s immune health. For most people, these infections are treatable with topical or oral antifungal medications, but early recognition and treatment are crucial.
Types of Fungal Skin Infections
1. Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis)
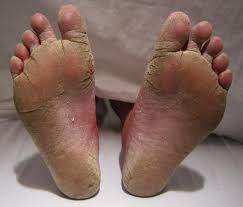
Athlete’s foot is one of the most common fungal infections, usually affecting the spaces between the toes. It thrives in warm, moist environments like sweaty socks, shoes, locker rooms, and public showers.
The infection often begins with redness, itching, and peeling of the skin, but in more severe cases, it can cause painful cracks (fissures), blisters, or even a burning sensation. If left untreated, the fungus may spread to the soles of the feet and toenails.
The condition is highly contagious and can spread through direct skin contact or by touching contaminated surfaces. Preventive measures include keeping the feet clean and dry, changing socks regularly, and wearing breathable footwear.
Antifungal creams, powders, and sprays are effective treatments, but in persistent cases, oral antifungal medications may be required.
2. Ringworm (Tinea Corporis)
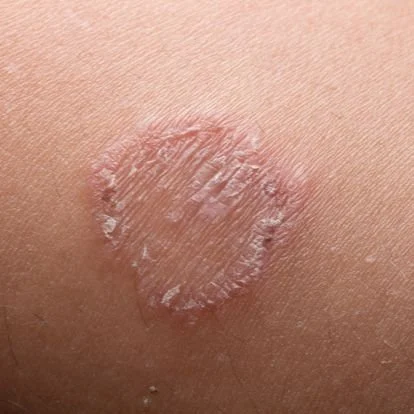
Ringworm is a fungal infection of the skin that gets its name from the characteristic ring-shaped rash it produces. The rash usually appears red and circular, with a slightly raised border and clearer skin in the center, giving it a “ring-like” appearance.
It can occur on different body parts, including arms, legs, trunk, and face, and often causes itching and discomfort.
The fungus spreads easily through skin-to-skin contact, sharing clothing, towels, or bedding, and even from infected pets. Maintaining personal hygiene and avoiding contact with contaminated objects are key preventive steps.
Treatment generally includes topical antifungal creams or ointments, while more severe or widespread infections may require oral antifungal medication.
3. Jock Itch (Tinea Cruris)
Jock itch affects the warm, moist areas of the body, particularly the inner thighs, buttocks, and groin. It is common among athletes, people who sweat excessively, or those who wear tight clothing.
The infection typically presents as red, itchy, and sometimes scaly patches that may form a ring-like pattern. The rash may worsen with exercise, heat, or friction from clothing.
While uncomfortable, jock itch is not usually serious and can be treated with over-the-counter antifungal powders or creams.
Good hygiene practices, such as keeping the groin area dry and wearing loose-fitting clothes, are essential for both prevention and treatment. If untreated, the infection may persist or spread to other parts of the body, including the thighs and abdomen.
4. Nail Fungus (Onychomycosis)
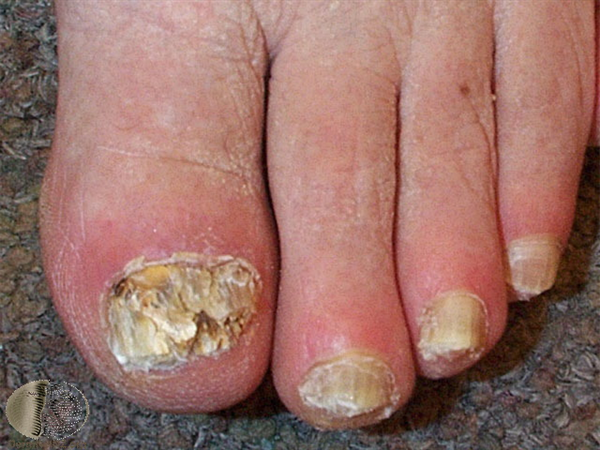
Nail fungus is a stubborn infection that affects the fingernails or toenails, though toenails are more commonly impacted. It begins as a small white or yellow spot under the nail and gradually spreads, causing the nail to thicken, discolor, and become brittle. In advanced stages, the nail may crumble, separate from the nail bed, or produce a foul odor.
Because nails grow slowly, nail fungus can be difficult to treat and may take months to clear completely. Topical antifungal nail solutions are available, but oral antifungal medications are often more effective.
Preventive measures include keeping nails trimmed, avoiding prolonged dampness, and wearing breathable footwear. In severe cases, removal of the infected nail may be recommended.
5. Scalp Ringworm (Tinea Capitis)
Scalp ringworm is a contagious fungal infection that primarily affects children, though adults can also get it. It causes scaly, itchy patches on the scalp that may lead to bald spots.
In some cases, pus-filled sores or black dots (broken hairs) may develop, giving the scalp a patchy appearance. The infection can spread to other parts of the body if scratched.
The fungus spreads through direct contact, contaminated objects such as combs, hats, or bedding, and even from infected pets. Because topical creams cannot penetrate the scalp deeply, oral antifungal medications are usually necessary for effective treatment. Good hygiene, not sharing personal items, and early treatment are key to controlling and preventing scalp ringworm.
What are the Causes Behind Fungal Skin Infections?
They are primarily caused by dermatophytes (fungi that feed on keratin), yeasts such as Candida, and certain molds. These organisms thrive in warm, moist, and humid conditions, which is why infections are more common in areas like the feet, groin, and armpits.
Everyday habits like walking barefoot in public showers, locker rooms, or around swimming pools can expose individuals to these fungi. Similarly, wearing tight or non-breathable clothing, especially in hot climates, creates the perfect environment for fungal growth.
Apart from environmental exposure, several risk factors make individuals more prone to fungal infections. People with compromised immune systems, diabetes, obesity, or excessive sweating are more vulnerable.
Poor hygiene practices, like not drying the skin properly after bathing or re-wearing sweaty clothes, also increase susceptibility. Since these fungi are contagious, they can spread through close skin contact, sharing towels, bedding, shoes, or even from infected pets.
Symptoms to Look Out For
The symptoms of fungal skin infections vary depending on the type and affected area, but there are some common warning signs. Persistent itching, redness, and flaky or scaly patches are often the first indicators.
- In conditions like ringworm, circular rashes with clearer centers are typical.
- An athlete’s foot may cause cracking and peeling between the toes.
- Nail fungus leads to thickened, brittle, or discolored nails, sometimes accompanied by discomfort.
- More severe symptoms may include blisters, pus-filled sores, or a noticeable foul odor from the infected site.
- In scalp infections, bald patches with broken hairs or crusty scales may appear.
The intensity of symptoms often depends on how quickly treatment begins; early treatment usually prevents the infection from spreading, while delays can make it widespread and harder to manage. Recognizing symptoms early is essential not only for effective treatment but also for stopping the spread to others.
Treatments for Fungal Skin Infections
Medical Approaches
Most fungal infections respond well to topical antifungal products like creams, sprays, ointments, or powders. These treatments are typically the first line of defense, and consistent application over a period of weeks usually clears mild cases.
However, for stubborn or extensive infections, oral antifungal medications such as terbinafine, fluconazole, or itraconazole are prescribed. These work internally to eliminate fungi that topical agents cannot reach.
Scalp fungal infections often require specialized medicated shampoos containing ingredients like ketoconazole or selenium sulfide, as creams cannot penetrate the scalp effectively.
Medical supervision is crucial during treatment, since misuse of antifungal medications or stopping treatment too early can result in recurrence. In some cases, untreated infections may even lead to secondary bacterial infections, further complicating recovery.
Home and Lifestyle Remedies
Alongside medical treatments, lifestyle changes play an important role in both healing and preventing fungal skin infections. Maintaining good hygiene is essential: skin should be kept clean and thoroughly dried, especially in folds or between toes.
Wearing loose, breathable fabrics helps reduce sweating, and changing clothes after exercise prevents prolonged dampness on the skin.
Some natural remedies may provide additional relief. Tea tree oil, known for its antifungal properties, can be applied in diluted form to affected areas, while aloe vera helps soothe itching and irritation.
However, these should never replace prescribed medications but rather serve as supportive remedies. Consistent self-care, when combined with medical treatment, significantly speeds up recovery and lowers the chances of recurrence.
ALSO READ
Seasonal Acne: Why Breakouts Change with Weather
Key Takeaway
While fungal skin infections are common and often frustrating, they are manageable with the right combination of medical treatments and lifestyle adjustments. Recognizing symptoms early, seeking medical care, and practicing preventive hygiene go a long way in reducing their impact. By staying consistent with healthy skin habits, you can lower your chances of recurrence and maintain better overall skin health.
FAQs
What are the most common types of fungal skin infections?
The most common include athlete’s foot, ringworm, jock itch, nail fungus, and scalp ringworm. Each has different symptoms, but they are caused by fungi thriving in moist conditions. Early detection and treatment help prevent complications.
How can I determine if I have a fungal skin infection caused by fungus or another skin condition?
Typical signs include itching, redness, scaling, and circular rashes. However, similar symptoms can occur in eczema or psoriasis. A dermatologist’s examination or skin scraping test can accurately confirm a fungal skin infection.
Is a fungal skin infection contagious?
Yes, most fungal skin infections are contagious. They can spread through direct skin-to-skin contact or indirectly via towels, shoes, or contaminated surfaces. Maintaining personal hygiene is crucial to avoid spreading them.
Can a fungal skin infection be permanently cured?
With proper treatment, fungal skin infection can be cleared, but recurrence is common if preventive steps aren’t followed. Long-term management includes hygiene, medication adherence, and avoiding environments that encourage fungal growth.


Join The Discussion