Skin Acne is one of the most common skin conditions across the globe, affecting nearly 85% of people between the ages of 12 and 24 at some point in their lives, according to the American Academy of Dermatology. While it is often associated with teenagers, adults can also experience acne well into their 30s, 40s, and even 50s.
Though not a life-threatening condition, acne can have a big emotional and social impact, lowering confidence and sometimes leaving permanent scars. Understanding what skin acne is, why it happens, and what its common symptoms look like is the first step toward managing it effectively. So, read on to explore the details.
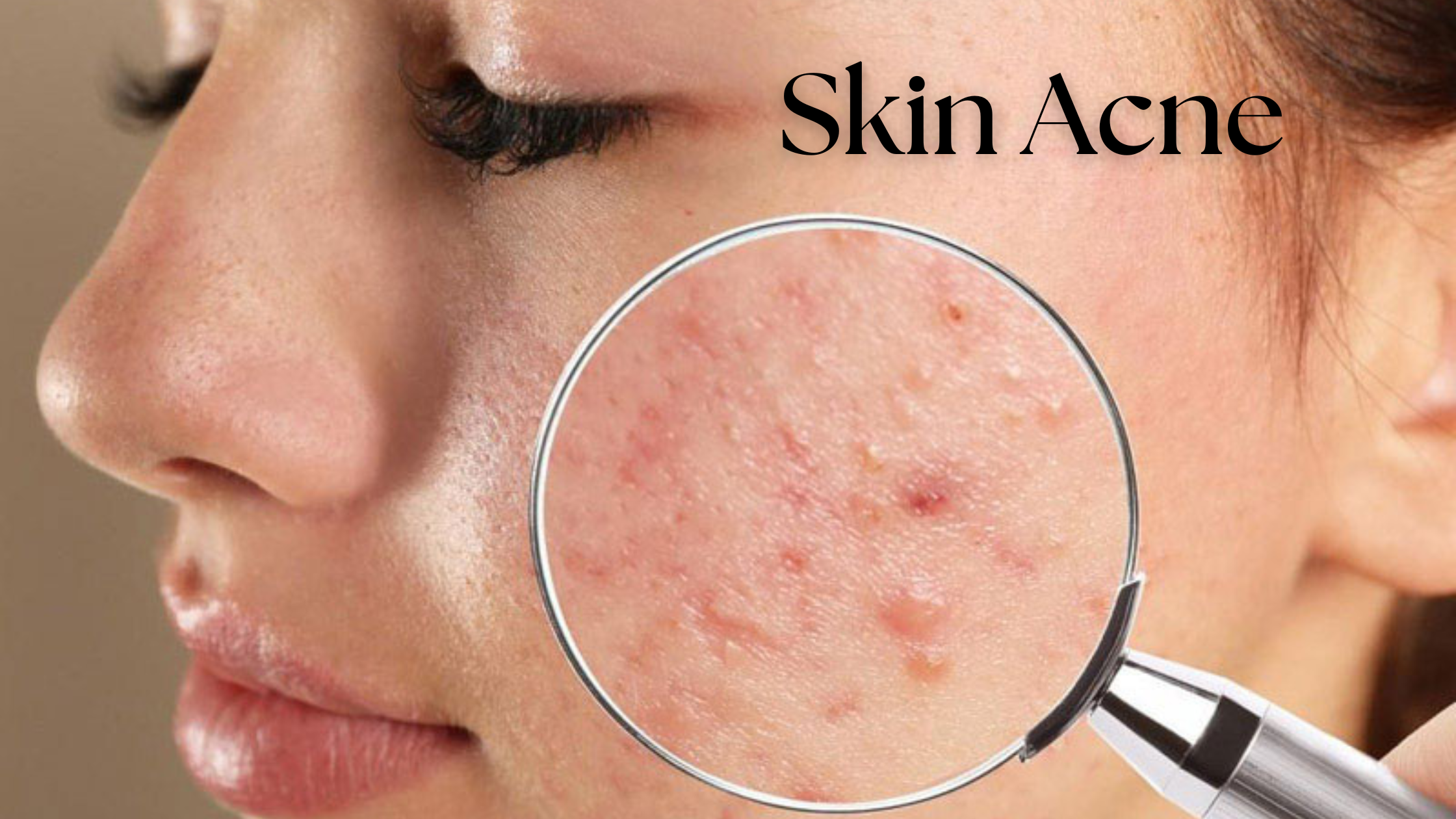
What is Skin Acne?
Skin acne develops when hair follicles (tiny pores in the skin) become blocked with excess oil (sebum), dead skin cells, and bacteria. This blockage leads to pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and sometimes deeper, more painful cysts.
Acne is most common on the face, chest, shoulders, and back, where oil glands are more active. While breakouts are temporary for some, others experience persistent acne that requires medical treatment.
For many people, acne is more than just a cosmetic issue; it can be painful, irritating, and emotionally challenging. Breakouts may flare up unexpectedly, often before important events or during stressful times, which adds to frustration. While mild cases might heal quickly, untreated or severe acne can leave lasting scars and impact a person’s confidence, making early care and awareness crucial.
What Causes Acne?
Acne doesn’t have a single cause; it results from a mix of biological and environmental factors. The most common include:
Excess Oil Production: Overactive sebaceous glands produce too much oil, clogging pores.
Hormonal Changes: Hormones (especially androgens) increase during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or stress, triggering breakouts.
Bacteria (Propionibacterium acnes): This bacteria multiplies in clogged pores, leading to inflammation and pus formation.
Dead Skin Buildup: Shedding of skin cells can block follicles and worsen acne.
Diet & Lifestyle Factors: Foods high in sugar, processed carbs, or dairy may worsen acne in some individuals.
Stress: Stress doesn’t directly cause acne, but it can trigger hormonal changes that make acne worse.
Common Symptoms of Skin Acne
Acne appears differently in each person, ranging from mild to severe. The most common symptoms include:
- Whiteheads: Small, closed clogged pores.
- Blackheads: Open pores clogged with oil and dead skin, appearing dark due to oxidation.
- Papules: Red, tender bumps that indicate inflammation.
- Pustules: Pimples filled with pus, red at the base and white/yellow at the top.
- Nodules: Large, solid, painful lumps beneath the skin.
- Cystic Acne: Severe, pus-filled lumps deep in the skin that often leave scars.
- Oily Skin: A shiny or greasy appearance due to excess sebum.
- Skin Tenderness: Irritation or pain in breakout areas.
ALSO READ
Skin Cancer Symptoms, Types, And Treatment In 2025
Types of Skin Acne
Acne is one of the most common skin conditions, but not all acne looks or feels the same. Dermatologists classify acne based on both its severity and its appearance, which helps in choosing the right treatment plan. Understanding the different types can make it easier to identify what you’re dealing with and when to seek medical advice.
Mild Acne
Mild acne usually appears as small whiteheads (closed comedones) and blackheads (open comedones). These are caused by clogged pores from oil, bacteria, and dead skin cells. In this stage, there are only a few inflamed pimples, and breakouts are often manageable with over-the-counter treatments and good skincare habits.
Moderate Acne
Moderate acne includes a greater number of papules (small red bumps) and pustules (pimples filled with pus). These can appear across larger areas of the face, chest, or back, making them harder to control with just basic care. At this stage, breakouts are more persistent, and dermatologists may recommend prescription creams or oral medications to reduce inflammation and bacteria.
Severe Acne
Severe acne is characterized by widespread, painful breakouts with nodules and cysts, large, deep, inflamed lesions that can leave scars if untreated. This form often requires medical attention, including stronger oral medications, hormonal treatments, or even procedures like chemical peels and laser therapy. Severe acne can significantly impact self-esteem, making timely treatment especially important.
What is Non-Inflammatory vs. Inflammatory Acne
Another way dermatologists categorize acne is by whether it’s inflammatory or not:
Non-Inflammatory Acne: Includes whiteheads and blackheads. These don’t cause much redness or swelling but can still affect skin texture.
Inflammatory Acne: Includes papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts. This type is more painful, visibly red, and more likely to cause long-term scarring.
Who is at Risk of Developing Skin Acne?
While almost everyone can develop acne, certain groups are at higher risk:
- Teenagers (due to puberty-related hormonal changes)
- Women (due to menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and hormonal fluctuations)
- People with oily skin types
- Individuals with family history of acne
- Those exposed to greasy products or high humidity environments
How is Acne Treated?
The treatment for acne depends on severity and skin type. Common methods include:
Topical Treatments: Creams or gels with benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or retinoids.
Oral Medications: Antibiotics, birth control pills (for women), or isotretinoin for severe acne.
Lifestyle Changes: Balanced diet, proper skincare routine, and stress management.
Professional Procedures: Chemical peels, laser therapy, and extractions performed by dermatologists.
How Does Skin Acne Impact Everyday Life?
Beyond physical symptoms, acne affects emotional well-being. Many people with acne report:
- Lower self-esteem and social anxiety
- Avoidance of public interactions
- Emotional stress, sometimes leading to depression
This makes acne not just a skin condition but also a mental health challenge, highlighting the importance of timely care and support.
Last to Say
Skin acne is one of the most widespread skin conditions, but it’s also one of the most misunderstood. From clogged pores to deep cysts, acne appears in many forms and is influenced by hormones, bacteria, and lifestyle factors. While symptoms may vary from blackheads to painful nodules, the emotional impact is often just as significant as the physical one.
With proper treatment, skincare, and lifestyle changes, acne can be managed effectively. Awareness and understanding are key not only to reduce breakouts but also to ease the stigma and boost self-confidence for millions of people worldwide.
FAQs
Can acne go away on its own?
Sometimes, yes. Mild acne may improve with age or simple skincare routines. However, persistent or severe acne often requires treatment to prevent scars and emotional distress.
Is acne caused by poor hygiene?
No. Acne is not about being “dirty.” In fact, washing too often or harshly can irritate the skin and make acne worse. It’s caused by oil, hormones, and bacteria.
Can diet affect acne?
Yes. Research suggests that high-glycemic foods (sugary snacks, white bread) and dairy may worsen acne for some people. A healthy, balanced diet often helps reduce breakouts.
What is the best treatment for acne scars?
Scars from acne can be treated with procedures like chemical peels, microneedling, and laser therapy. Early acne treatment helps prevent scarring in the first place.
Can stress make skin acne worse?
Yes. Stress triggers hormonal changes that can lead to flare-ups. Managing stress with sleep, exercise, and mindfulness can improve skin health.
Sources: American Academy of Dermatology Association


Join The Discussion