Cancer remains one of the most pressing health challenges worldwide, affecting millions of people every year. In 2025, cancer continues to be a leading cause of death, with some types of cancer, such as lung, breast, colorectal, and prostate cancer, accounting for a majority of cases. While medical science has made significant advances in early detection and treatment, awareness remains the most powerful tool in reducing risk and improving survival rates.
Recently, global conversations around cancer prevention have been reignited when celebrity chef Gordon Ramsay revealed his skin cancer diagnosis. The “Hell’s Kitchen” star underwent surgery to remove basal cell carcinoma from his jawline and urged the public to take sun protection seriously by wearing sunscreen. His story serves as a timely reminder that cancer can affect anyone and that simple precautions, like shielding skin from harmful UV rays, can save lives.
This blog explores the most common types of cancer in 2025, their symptoms, and the importance of awareness and prevention.
What is Cancer?
Cancer is not a single disease but a group of diseases characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the body. These cells may form tumors (solid masses) or spread through the blood and lymphatic systems, interfering with normal body functions. If not detected and treated early, cancer cells can invade nearby tissues or metastasize (spread) to other organs, making treatment more challenging.
Most Common Types of Cancer Worldwide in 2025
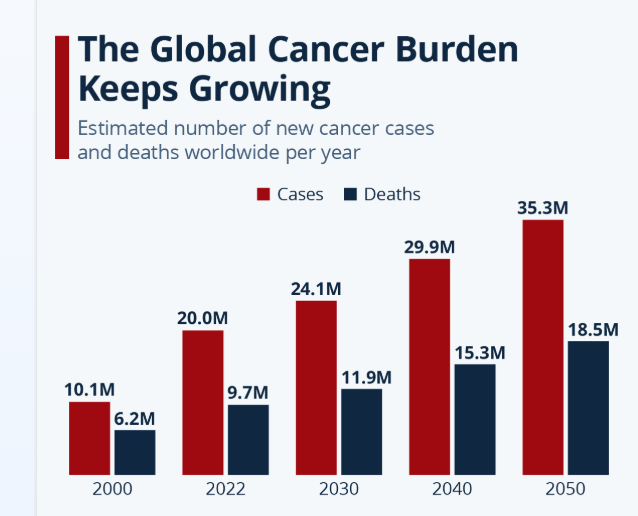
Image Sources: Statista
Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer occurs when malignant cells develop in the tissues of the bladder. Smoking and exposure to harmful chemicals are among the key risk factors. Symptoms often include blood in the urine, frequent urination, and pelvic pain.
Breast Cancer
Still one of the most diagnosed types of cancer worldwide, breast cancer primarily affects women, though men can also develop it. Regular self-exams, mammograms, and genetic screening play a crucial role in early detection.
Colon and Rectal Cancer (Colorectal Cancer)
A leading cause of cancer deaths globally, colorectal cancer often develops silently over time. Risk factors include poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, and family history. Colonoscopies remain vital for prevention and timely treatment.
Endometrial Cancer
This cancer begins in the lining of the uterus and is most common in postmenopausal women. Risk is often linked to obesity, hormonal imbalances, and family history. Early symptoms usually involve abnormal bleeding.
Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer rates have been rising, with smoking, high blood pressure, and obesity serving as key risk factors. Early stages often go unnoticed until imaging tests reveal tumors.
Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer begins in the cells lining the cervix, the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. It is most often caused by persistent infection with high-risk strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). Early stages usually show no obvious symptoms, But, when symptoms do appear, they may include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, or pain during intercourse. With vaccination, routine screening, and timely treatment, cervical cancer is one of the most preventable and treatable types of cancers worldwide.
ALSO READ
Pakistan Launches First National Cervical Cancer Vaccination Drive
Leukemia
A cancer of the blood and bone marrow, leukemia affects both adults and children. It disrupts the production of healthy blood cells and often requires long-term treatment, including chemotherapy and bone marrow transplants.
Liver Cancer
Most common in areas with high rates of hepatitis infections, liver cancer is also linked to alcohol use and fatty liver disease. Prevention strategies include vaccination against hepatitis B and managing liver health through lifestyle choices.
Lung Cancer
Among the deadliest types of cancer globally, lung cancer is strongly tied to tobacco use and environmental pollution. Symptoms such as chronic cough, chest pain, and difficulty breathing often appear in later stages.
Melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer, arising from pigment-producing cells in the skin. Excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays, whether from the sun or tanning beds, is the main culprit. Early detection can make melanoma highly treatable, but if ignored, it can spread aggressively.
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
This cancer starts in the lymphatic system and affects the body’s ability to fight infections. Risk factors include a weakened immune system, viral infections, and age. Treatment may involve chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy.
Pancreatic Cancer
Known for its aggressive nature, pancreatic cancer is often detected late because symptoms develop subtly. It is one of the hardest cancers to treat, underscoring the need for more research and improved screening tools.
Prostate Cancer
A leading cancer among men, prostate cancer often develops slowly. Routine screening, especially for men over 50, is crucial for early detection. Treatments vary depending on severity, from watchful waiting to surgery and radiation.
Thyroid Cancer
Cases of thyroid cancer are rising worldwide, especially among women. It develops in the thyroid gland and is often detected through imaging tests. Fortunately, many forms of thyroid cancer are highly treatable with surgery and radioactive iodine.
The Bigger Picture
While medical science has advanced rapidly, cancer remains one of the greatest public health challenges in 2025. Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, eating a balanced diet, staying active, and protecting skin from UV rays, can reduce risks significantly. Public figures like Gordon Ramsay sharing their health battles shed light on how vital prevention and awareness are, especially with conditions like skin cancer that often go unnoticed until advanced stages.
In short, knowledge is one of the strongest tools against all types of cancer. By recognizing the most common types, understanding risk factors, and taking preventive measures, individuals can take control of their health and improve their chances of early detection and effective treatment.
FAQs
What are 20 warning signs of cancer?
Common warning signs include unexplained weight loss, persistent fatigue, lumps or swelling, skin changes, unusual bleeding, prolonged cough, difficulty swallowing, changes in bowel habits, night sweats, loss of appetite, chronic pain, frequent infections, anemia, changes in urine, jaundice, unexplained fevers, shortness of breath, hoarseness, abnormal discharge, and neurological changes. If these symptoms persist, medical consultation is vital.
Can you survive stage 4 cancer?
Yes, survival is possible depending on the type of cancer, treatment response, and overall health. While stage 4 is advanced and harder to treat, new therapies like immunotherapy and targeted treatments have improved survival rates for some patients.
What is 90% of cancer caused by?
Around 90% of cancers are linked to lifestyle and environmental factors such as tobacco use, poor diet, alcohol consumption, obesity, infections, pollution, and prolonged UV exposure, highlighting the importance of preventive care.
What are the 4 types of cancer?
The four main categories of cancer are:
- Carcinomas – cancers of organs and glands (e.g., breast, lung, colon).
- Sarcomas – cancers of connective tissue (e.g., bone, muscle).
- Leukemias – cancers of the blood and bone marrow.
- Lymphomas – cancers of the immune system.
What causes cancer?
Cancer is caused by genetic mutations that disrupt normal cell growth. These mutations can result from inherited genes, lifestyle habits (like smoking, poor diet), infections, environmental exposures (radiation, chemicals), and aging.
How fast can cancer spread?
The speed of cancer spread depends on the type. Aggressive cancers such as pancreatic, lung, and liver cancer can spread within weeks or months, while slower types like prostate cancer may progress over years. Early detection greatly improves treatment outcomes.
Sources: NIH, Statista, Washington Post


Join The Discussion